






 find out
find out
find out
find out
find out
find out









| Quantum Computing News from MIT |
| Lectures |
| Speed of Quantum Computers |
| Quantum Cloud Computer |
| Quantum Computers in Business |
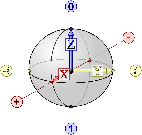
| Requirements of a Qubit |
| Quantum Computing Degrees |
| Quantum Computing Videos |
| What is Cloud-Computing? |
| When Will I Be Able to Buy a Quantum Computer? |
| Examples of a Qubit |
| University Quantum Computing Programs |
| Future of Quantum Computing |
| Qudits or Qubits |
| Quantum Cryptography |
| Quantum Q&A |
| How will quantum computers affect my life? |
| What is the History of Quantum-Computing & Quantum-Computers? |
| What is the future of quantum computing? |
| Who Needs a Quantum Computer? |